Detailed examples have been provided for common scenarios such as adjusting for physical inventory counts, inventory shrinkage, obsolete inventory, and consignment inventory. These examples illustrate the practical application of adjusting journal entries and highlight the importance of accurate inventory accounting. Accurate and timely adjusting journal entries for inventory are essential for maintaining reliable financial records. This inventory accounting journal entry is where production-related expenses for your inventory such as rent, utilities, storage, and materials used in the manufacturing process are recorded. The entry debits your manufacturing overhead and credits your raw materials inventory to record your indirect material costs.
Journal Entry for an Inventory Purchase
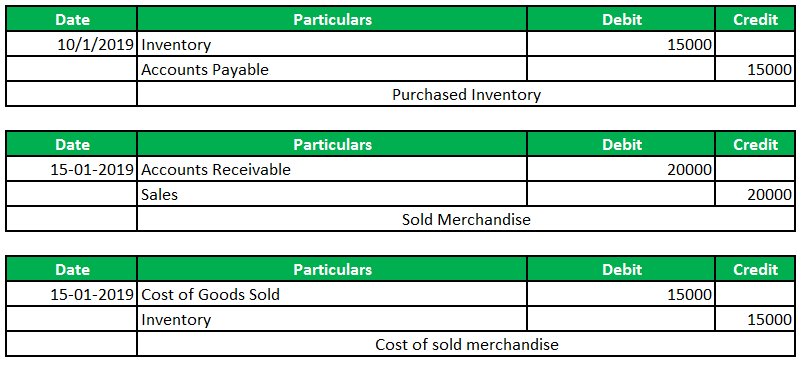
This entry typically involves debiting the Inventory account to increase the company’s assets, showing that inventory has been added to the stock. Under the periodic system, the company can make the journal entry of inventory purchase by debiting the purchase account and crediting accounts payable or cash account. Accurate inventory adjustments are critical for maintaining the integrity of financial statements and ensuring the financial health of a business.
Periodic vs Perpetual Inventory System Journal Entries
- We do not record any expense as the company already estimate and record in the prior month.
- On 31 Mar 202X, the inventory balance is $ 500,000, and management estimate inventory write-down of $ 5,000 which may cause by various reasons such as obsolete and damage.
- An accounting journal is a detailed record of the financial transactions of the business.
- He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own.
- Once the necessary adjustments have been calculated, prepare the journal entries to update the inventory records.
This entry adjusts the inventory account to match the actual physical count and records the shrinkage as an expense. You report inventory obsolescence by debiting the relevant expense account and crediting the opposing asset account. An inventory write-off expense account records the value of any damaged inventory that cannot be sold. Inventory may be lost because of spoilage or other factors in the manufacturing process. While the cost of common inventory spoilage may initially be recorded as an asset, it will later be charged to your expenses in a subsequent accounting period.
Physical Inventory Counts
A perpetual inventory system keeps continual track of your inventory balances. Not to mention, purchases and returns are immediately recorded in your inventory accounts. Finally, we have to ensure that inventory reserve is eliminated if the company gets rid of all inventory what are noncash expenses meaning and types on balance sheet. If we do not eliminate the reserve inventory, it will show the negative balance on the balance sheet as the inventory is already zero. So when we sold all inventory on balance sheet, we have to ensure that the inventory reserve is zero too.
If you’re using a purchase account, add the balance of that account to the beginning inventory total, then subtract the costed ending inventory total to arrive at the cost of goods sold. Journal Entry for Inventory DiscountsLets assume that the vendor has terms that state a discount will be given on the inventory for early payment, perhaps within the first 30 days following delivery. If your entity makes payment during this window, then ultimately this needs to find its way into the financials. The best way to go about doing this is to eliminate the liability for Accounts Payable from the books at what you originally recorded it for. The amount of cash paid must be removed from the books, and the cost of the inventory will need to be reduced in order for it to be recorded at the cost paid.
Perpetual vs periodic inventory accounting methods
Compare the physical inventory counts with the recorded inventory levels in the accounting system. Calculate the total value of the discrepancies to determine the necessary adjustments. As well as recording your expenses, inventory accounting journal entries must also record your sales. Sales transaction entries record any profits from the sale of finished goods.

The potential inventory related transactions for a retailer would include the purchase of inventory, purchase discounts on inventory, and sale of inventory. When the work is completed, the $100 is debited to the finished goods inventory account. To simplify the illustration, all items are assumed to have had the same cost, $2.00. Also, as already noted, some perpetual records maintain only a record of units. Perpetual inventory systems have been enhanced in recent years using computers and electronic point of sale devices such as credit card readers. Management is, therefore, always aware of inventory levels and can make timely purchases that ensure the desired inventory levels.
Properly adjusted inventory accounts reflect the true value of inventory, providing a reliable basis for financial reporting, operational decision-making, and tax compliance. Accurate inventory records help avoid overstated or understated financial positions, which can mislead stakeholders and result in poor business decisions. Understanding the different types of inventory, the methods used for their valuation, and their impact on financial statements is crucial for accurate financial reporting and effective business management. This knowledge forms the basis for making precise adjusting journal entries, ensuring that a company’s inventory records and financial statements are reliable and accurate.
Inventory is listed on the balance sheet as a current asset, indicating its importance in the company’s financial health. Accurate inventory accounting is vital because it affects the cost of goods sold (COGS) and, subsequently, the company’s gross profit and net income. Proper inventory management ensures that the business can meet customer demand without overstocking, which ties up capital, or understocking, which can lead to lost sales. Identifying inventory shrinkage involves comparing physical inventory counts to recorded inventory levels. The journal entry typically involves debiting an expense account, such as “Inventory Shrinkage Expense,” and crediting the inventory account to reflect the loss.
